Procedures for trademark application in Japan
- 1.Power of Attorney
-
- After initial consultations, our firm will send a request document to the client for completion. The client shall provide the character, sign or figure for trademark registration application as well as the commodity and service.
- 2.Pre-filing research and trademark search
-
- The trademark search will be conducted based on the desired mark. In case of any identical or similar registered trademark, the application may be refused. Therefore, our firm will raise new application suggestions for you if there is any similar registered trademark so as to avoid such similarities. Furthermore, we will conduct research on the distinctiveness of the trademark and other trademark requirements in advance.
- ※ The basic procedures of trademark registration application include the pre-filing research and easy search service
- ※ Our firm may provide the pre-filing research and basic search service separately from the application. For example, if registration is less possible according to the pre-filing search results and the client decides to withdraw the application, we will only charge the service fee for such search, i.e., JPY 10,000
- 3.Preparation for trademark registration application
-
- Our firm will prepare the documents for trademark registration application according to the trademark search results and based on the client’s opinions and may amend such documents as required by the client. Many technical words and terms will be used in this stage, please contact us in case of any question.
- 4.Application for trademark registration
-
- Upon confirmation of the trademark registration application documents by the client, our firm will file such application online to the Japan Patent Office and then will send the official filing receipt to the client. The application number in Japan will be issued by the Japan Patent Office at the same time.
- 5.Disclosure of the Application
-
- Upon application of the trademark, the Japan Patent Office will disclose the details of such trademark registration application.
- ※ Once the trademark application is published, the applicant is given the right to warn or make any claim for compensation against any unauthorized user of the trademark.
- 6.Examination Stage
-
- Upon submission of the trademark application to the Japan Patent Office, the case will be examined. The Patent Office will review whether there is any similarity issue in regards to any registered trademark and whether there is any distinctiveness of the trademark as filed, and after a certain period of time will send a notice of registration approval or an Office Action. In case of an Office Action, our firm may provide you with further professional response services (amendment / argument).
- Amendments may be made with respect to the parts of a certain commodity or service which are similar with any registered trademark, or by deletion or reduction.
- Argument is made to clarify the reasons why the trademark under application is not similar with any registered trademark or is not a descriptive trademark so as to be obtain the grant of right.
- Pursuant to the trademark system, if there is any identical or similar registered trademark which has not been used for a certain period of time, the applicant may apply to revoke such registered trademark on the ground that such trademark has not been used, and thus eliminate the reasons for refusal.
- Additionally, even if the application received a Final Rejection during the examination stage, the applicant may still file an Appeal to the Patent Office during the trial stage. For example, the applicant may make try clarifying that the trademark as filed will not be confused with any registered trademark by means of any specific trade case, or by proving the distinctiveness of the trademark by means of the results of the trademark’s use.
-
※ The fees for filing a response include the fees for filing argument (JPY 50,000) and the fees for filing amendments (JPY 50.000).
Such fees may vary depending on the case. Please contact us by email for further details.
- 7.Trademark registration procedures
-
- We will handle the registration procedures before the Office upon receiving the Notice of Allowance. The applicant may choose either a five or ten years’ duration of the right and may also obtain a semi-permanent trademark right through regular renewal.
- 8.Procedures for trademark right maintenance
-
- You may obtain a semi-permanent trademark right by submitting a renewal application during the renewal period of the trademark right, and may benefit from the system of installment payment over five years during the course of payment of registration fee or application for renewal.
- Tsubame IP Law Firm can provide a written management and reminder service with respect to the renewal period and the period of installment payment to any client who authorizes our firm to undergo the procedures of trademark right registration.
- Furthermore, Tsubame IP Law Firm can also provide services for trademark right renewal. For details, please click “Trademark Renewal Service”.
Steps to obtain a trademark right
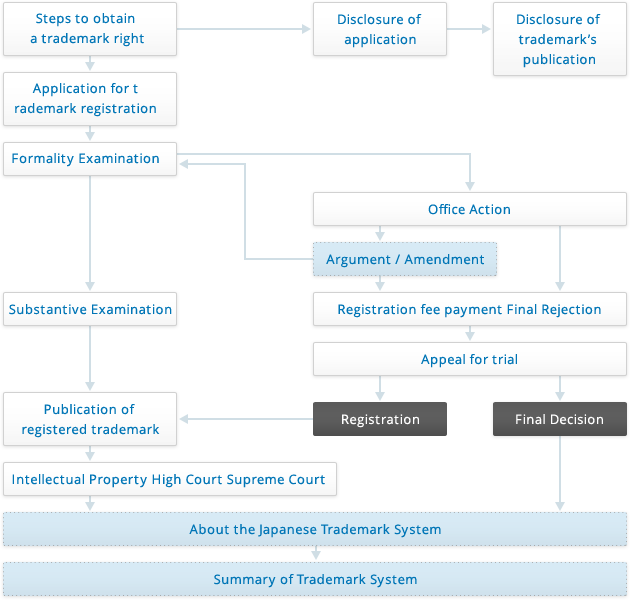
Fees for basic procedures of trademark registration application
- ※ From second classification, attorney fees of USD 450 and official fees of USD 78 would be incurred incrementally.
- ※ If the number of designated goods/services exceeds 10, a translation fee of USD 4 for each item would be incurred.
Summary of Trademark System
- 1.A trademark right refers to the exclusive right to use the trademark connected to certain commodities or services.
- The use of trademark refers to the marketing and promotion of certain commodities affixed with such trademark and the use of such trademark in certain services (e.g., a catering business uses the trademark on its tableware while providing its services) and adverting signs. If there is no connection between the trademark and the specific commodities or services, the trademark cannot be registered. In case of unauthorized use of the registered trademark by a third party, the owner of such registered trademark may force such the party to cease such use by exercising its trademark right and make a compensation claim.
- 2.The trademark right exists in different countries independently.
- Therefore, you must apply for the trademark right to the Japan Patent Office if you want to obtain a Japanese trademark. As to the procedures to apply for the right and manage a trademark in Japan from a foreign country, you may apply directly to the Japan Patent Office or through the competent government authority in your homeland in accordance with the Madrid Protocol. Tsubame IP Law Firm also provides services with respect to the notice of refusal under the Madrid Protocol.
- 3.Any trademark which is identical or similar with any registered trademark or may be confused with any business of anyone cannot be registered.
- The trademark right is exclusive, i.e., a registered trademark cannot be registered again. Any trademark of a third party which is not registered but has gained a certain reputation cannot be registered either.
- 4.Any geographical name without any distinctiveness or any descriptive trademark which describes the nature of certain commodity without any distinctiveness cannot be registered.
-
Any single color trademark, any trademark without any distinctiveness such as ○ or ▽, any geographical name such as “Tokyo Tower” or “Echi-go”, or any descriptive trademark such as “delicious” or “warm” which describes the nature of certain commodity, is not consistent with the exclusivity of trademark and cannot be registered.
However, a geographical name or descriptive trademark may be registered if there is any result of the use of such trademark (item 2 of Article 3 of the Trademark Act). A trademark consisting of a geographical name and a descriptive trademark (e.g., Echi-go Beer (JP Trademark No. 449710) and Delicious Calcium Life (JP Trademark No. 5011254)) may also have a possibility of registration. Furthermore, a trademark associating with a geographical name or the nature of certain commodity (e.g., Snow Country (JP Trademark No. 1674302)) and Oisix (JP Trademark No. 4271795)) may also have a possibility of registration.
Additionally, the combination of “a geographical name + commodity” may be registered as a collective trademark under certain circumstances. For example, Ooma Maguro (JP Trademark No. 5051377) and Wakayama Ramen (JP Trademark No. 5004520).
- 5.Three-dimensional trademark has been approved
- Except for characters, signs and figures, any three-dimensional trademark is also protected by the trademark system. For example, Peko-Chan, a character trademark affixed to a commodity, and the form of a commodity may become a three-dimensional trademark. An example for the commodity form itself registered as a trademark is MAGLITE. Since the trademark right could exist semi-permanently, from now on we should handle the right of the three-dimensional trademark with strategic thinking.
- 6.“Dynamic Trademark” has been approved
-
Any changing character and figure played on the screen of TV and computer and any sign which will change over time are within the scope of the trademark registration (see the example below). For example, the frame of a roaring lion, which is played at the beginning of any film made by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc, a film and television program distribution company, is a classic example of a dynamic trademark. Except for the dynamic two-dimensional trademark, there are also the dynamic signboards and other dynamic three-dimensional trademarks. During the examination, a sign trademark and a dynamic trademark in which such sign keeps moving alone may be deemed as this type of trademark.
 The above reference example of dynamic trademark is quoted from the homepage of the Japan Patent Office.
The above reference example of dynamic trademark is quoted from the homepage of the Japan Patent Office.
The number in the Figure means the order of change.
- 7.Hologram trademark
-
Any character or figure which seems changing from different viewing angles by way of a hologram and any other way also falls within the scope of the trademark registration. During the examination, if what you see from any certain viewing angle of a character and figure is identical or similar with any existing trademark, such character and figure cannot be registered.
 A reference example of hologram trademark is quoted from the homepage of the Japan Patent Office.
A reference example of hologram trademark is quoted from the homepage of the Japan Patent Office.The numbers in the above figure are to show what you will see from different angles. For example, figure 1 is the view from the left, figure 2 is the view from the front, and figure 3 is the view from the right.
- 8.Trademark consisting only of color(s)
-
A trademark consisting of a single color or several colors is also a subject of trademark registration. A trademark which is a combination of figure and color is always a subject of trademark registration, and now a trademark consisting only of color(s) is also possible to become a registered trademark, e.g., a color(s) used in packaging paper and poster of a commodity. However, a color trademark cannot be recognized as a registered trademark in principle, unless a certain commodity using merely color(s) has achieved such a strong influence that anyone can associate such color with such commodity and such influence has become national. Only under such circumstances could such color be registered as a trademark.
 This reference example of trademark is quoted from the homepage of the Japan Patent Office.
This reference example of trademark is quoted from the homepage of the Japan Patent Office.
- 9.Sound trademark
-
A sound trademark refers to the sound used in any advertisement as well as boot-up music, voice and natural sound. It can be distinguished through hearing and is the subject of trademark registration. A sound will be deemed indistinctive in principle and cannot be registered as a trademark if it is the sound made by a commodity generally, or a single tone, or the sound which will be distinguished as a natural sound, or the sound which is only music without a second implication. A trademark consisting of the pronunciation of the character trademark will be deemed as similar with such character trademark.
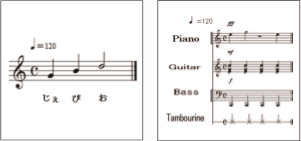
- 10.Position trademark
-
A position trademark means a trademark consisting of a figure or any other sign and the position of such sign in a commodity. The sign may be registered as a common trademark if such sigh itself is distinctive. If the sign itself is indistinctive, it may acquire the distinctiveness by fixing such sign in a particular position in a commodity. We would like to introduce such a trademark through the following registration cases.
USA trademark registration No. 2363544
-

Registration case
-

Use case
The registered trademark case: the red cursor control device in the keyboard of IBM (now Lenovo) computer. The red cursor control device is only a red round shape without any distinctiveness. Once it is used in certain position of the computer keyboard, the clients will clearly identify that this is a computer keyboard made by IBM.Europe trademark registration No. 1027747
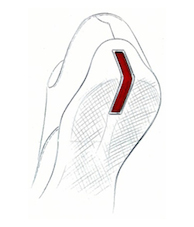 The design of “the heel with a red line” in PRADA shoes has been registered as a position trademark in Europe. The red line alone is indistinctive, but if it is fixed into a certain position on a shoe, consumers will clearly identify that these shoes are of PRADA.
The design of “the heel with a red line” in PRADA shoes has been registered as a position trademark in Europe. The red line alone is indistinctive, but if it is fixed into a certain position on a shoe, consumers will clearly identify that these shoes are of PRADA. -